|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chief Editor
|
||
|
ALCOHOL,
A DOUBLE-EDGED SWORD There has been a spate of research that encourages
moderate alcohol drinking. But these studies do not provide us with the
adverse effects of alcoholism. It is important to know the bad side effects
of a drug before we use it for the beneficial effects. However, researchers report that alcohol itself,
however, was not the key. Instead, the plant-derived hops that give beer its
bitterness could be responsible. In “Moderate alcohol consumption may have important
health benefits in terms of reducing the risk of ischemic stroke [i.e.,
they may not
have important health benefits]," concludes a team of
researchers3. Previous studies have suggested that alcohol
protects against heart disease by helping to raise blood levels of High Density Lipoprotein (HDL). However, the Japanese
investigators found no such
association in their study. But the authors also note that "heavy
drinking (five or more drinks per day) was associated with (a 37%) increased
risk of stroke." And they say the consumption of seven or more drinks
per day pushed stroke risk to a level more than triple that of abstainers. The
so-called benefits claimed for alcohol are essentially due to the presence of
plant derived antioxidants and hops. Resveratrol is part of a group of
compounds called polyphenols. They’re thought to act like antioxidants,
protecting the body against damage that can put you at higher risk for things
like cancer and heart disease. It is in the skin of red grapes, and as a
result, it is found in wine. Resveratrol is found in grapes, wine, grape
juice, peanuts, cocoa, and berries of Vaccinium species, including
blueberries, bilberries, and cranberries.
Resveratrol activates the SIRT1 gene that protects the body against
the effects of obesity and the diseases of aging. Dr.
Gregory N. Larkin4 advices: Alcohol has been a societal libation
for centuries rendering both benefits and trauma to those who drink it. The
definition of what constitutes a drink is beer = 12 ozs., wine = 5 ozs., 80
proof distilled spirits =1.5 ozs. Following are some
characteristics and guidelines regarding alcohol effects: The risks of liver
damage (cirrhosis), pancreatitis and certain types of cancers (mouth, liver,
throat, larynx and the esophagus). Long-term heavy consumption can also cause
loss of appetite, vitamin deficiencies, stomach problems, skin problems,
sexual impotence, obesity, and heart, central-nervous-system and psychological
disorders. Heavy drinking also increases death from automobile and
recreational accidents, harmful fetal development, and the incidence of
homicide and suicide. ·
if you have not started yet ·
if you are pregnant or anticipate pregnancy ·
if you have medical conditions like liver disease
or ulcers ·
if you have a family history of alcoholism ·
if you are taking medications that interact with
alcohol ·
if you anticipate activities that require alertness |
||
|
REFERENCES AND NOTES [1] డాక్టర్ శ్రీనివాసరావు వేపచేదు | डॉक्टर श्रीनिवासरावु वेपचेदु |
Dr. Sreenivasarao Vepachedu https://www.linkedin.com/in/vepachedu/
2 Arimoto-Kobayashi et al., Inhibitory effects of
beer and other alcoholic beverages on mutagenesis and DNA adduct formation
induced by several carcinogens, Journal Agricultural Food Chemistry 47, 221 –
230 (1999). https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/jf980685a Abstract: The possibility that beer and other alcoholic
beverages could be antimutagenic against the heterocyclic amines (HAs), a
group of carcinogens produced on cooking proteinaceous foods, has been
explored. In the Salmonella mutation assays, beer showed inhibitory effects
against several HAs [preactivated Trp-P-1,
Trp-P-2(NHOH), and Glu-P-1(NHOH)] that are directly mutagenic in bacteria.
Japanese sake, red and white wines, and brandy were also effective. However,
ethyl alcohol alone did not show these effects. The formation of O6-methylguanine
by N-methyl-N‘-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in the DNA
of Salmonella YG7108 was also inhibited by beer. Nonvolatile beer components
were administered orally to CDF1 mice together with Trp-P-2. Adducts in the
liver DNA were significantly decreased by the beer, as compared to those in
controls fed Trp-P-2 only. Although several phenolic compounds known to be
present in beer were antimutagenic toward these mutagens, their effects were
very small. It was concluded that some yet to be identified component(s) of
beer is (are) responsible for this antimutagenicity. Antioxidative
activity of hop bitter
acids and their
analogue has a
cancer preventive effect
since they can block free radicals which cause
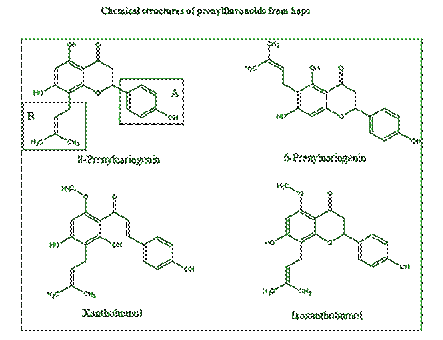
oxidation of the DNA in the body Stevens et al., Fate of xanthohumol and related
prenylflavonoids from hops to beer, J Agric Food Chem. 47(6):2421-8 (1999).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10794646
Miranda et al.,
Prenylflavonoids from Hops Inhibit the Metabolic Activation of the
Carcinogenic Heterocyclic Amine 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline, Mediated
by cDNA-Expressed Human CYP1A2, Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 28 (11)
1297-1302 (2000). http://dmd.aspetjournals.org/content/28/11/1297
[3] The Protective Effect of
Moderate Alcohol Consumption https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/8c02/753c18c1ed86e75d0c6b4c4933c6f597a528.pdf
[4] Dr. Gregory
N. Larkin, MD, Director of Corporate Health Services, Eli Lilly and Company, 1999 https://www.science.gov/topicpages/r/reduce+alcohol-related+harm.html
Have a possible problem with alcohol usage? Discuss your concern with your doctor and get help from
support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous. Here are some web sites that might
be helpful:
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Alcohol Abuse Amongst The
Elderly: A Complete Guide Alcoholism Addiction Treatment Alcohol Addiction
(Healthline) Alcohol Use Disorder
(Medline) Drug & Alcohol Addiction
Treatment |
Copyright ©1998-2018,
Vepachedu Educational Foundation, Inc.
ॐ असतो मा सद्गमय । तमसो मा ज्योतिर्गमय । मृत्योर्मा अमृतं गमय । ॐ शान्तिः शान्तिः शान्तिः ॥